Were you lucky enough to buy Apple stock (AAPL*) on April 8, 1983, for $0.18 and, more impressively, still hold it?
Or did you receive stock options from Microsoft (MSFT*) when you worked there in the early 1990s for $1 a share?
While these are good problems to have—Taylor Swift would say "Champagne Problems"—they potentially leave you with a riskier portfolio or a large tax bill if you sell them. So how should you handle a significant, appreciated stock position?
Problems with a concentrated stock position
A concentrated position in any one security can pose two distinct problems.
Problem 1: The inherent risk of having a substantial portion of your wealth tethered to one company. This risk highlights the concept of diversifiable vs. nondiversifiable risk. Investors can diversify specific risk from one company by holding more than one security. For example, research shows that holding roughly 20 stocks potentially can diversify away about 80% of the risk.1 But even if you have 20 or more stocks, a single company concentration may limit the impact of that diversification—losing the punch you hoped it could deliver.
Problem 2: Diversifying a large, appreciated position often triggers a significant tax bill. Even if you recognize that you're overly concentrated in one stock, reducing exposure is complex. One of the downsides most people want to avoid is paying capital gains tax on the sale of a sizeable stock gain.
While there are no easy solutions, there are options to dilute the unwanted intensity from such a large position.
Concentrated risk solutions
De-risking considerable exposure to one company typically requires complicated financial maneuvering. Several methods focus on limiting the effects of a downside move or protecting against a steep decline in the stock. For example, some investors hedge their position with equity options. A common strategy is to employ an equity collar—which is to say they buy put options and sell call options on the stock. Buying a put option provides downside protection, while selling a call option gives the investor income. Of course, an equity collar is just one risk-mitigation strategy. Additional strategies involve other derivatives, like forward contracts.
In addition to protecting against downside risk, some investors attempt to capture the upside simultaneously. An example is to participate in an exchange fund where investors pool concentrated shares and each investor receives a slice of the pool.
Again, these are complex ways to minimize the risk and often require meeting specific criteria, rules, and regulations, so consult with a Wealth Advisor or investment professional.
Diluting exposure without triggering a massive tax bill
There’s no simple way around selling appreciated stock while you’re alive and not paying long-term capital gains tax. So what should you do?
Here are five tax-mitigating strategies that may work for you.
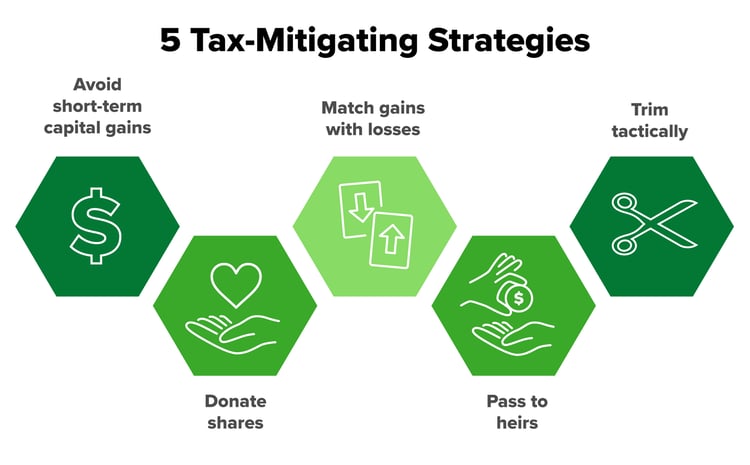
- Avoid short-term capital gains. In many cases, the shares may be long-term holdings. But if they aren't, consider maintaining the position for longer than a year so you don’t face the higher short-term capital gains tax rate. The difference between long and short-term capital gains tax rates can be substantial.
- Donate shares to a qualified charity. Instead of giving cash donations, consider gifting your appreciated securities. This strategy lets you avoid the capital gain tax on a sale while you keep the cash to invest in a more diversified manner. And you may also receive a tax deduction for the gift—a 1-2-3 punch!
- Match gains with losses. This strategy—commonly known as tax-loss harvesting—attempts to offset your taxable gains on the sale of an appreciated security by selling a stock for an equivalent loss.
- Pass to heirs upon your death. Leave the appreciated securities in your estate so that when you pass, their value steps up in cost basis and becomes a tax-efficient wealth transfer.
- Trim tactically. Evaluate and reduce the position each year, putting the proceeds from a sale into a diversified portfolio. Look at it this way: You only need to get rich once! So by selling a substantial gain over time, hopefully, you can "stay rich." The annual evaluation would occur at the end of the year, so your Wealth Advisor could most accurately determine your capacity for additional income after accounting for all other income throughout the year and potential tax-loss harvesting opportunities.
As with any tax strategy, you should always consult a tax professional before making these or other tax decisions. Motley Fool Wealth Management can counsel on tax efficiency and general tax considerations but does not (and is not permitted to) provide tax advice.
You have choices
As we said earlier, a concentrated, appreciated stock position is enviable. But it also requires diligence and care to unwind properly. Fortunately, you have options.
So whether you’re looking to hedge your risk, dilute your exposure, or perhaps both, we believe it’s best to work with a Wealth Advisor to understand how doing so may fit into your overall wealth plan.
For example, gifting a concentrated position may make sense if you have legacy aspirations. But suppose you prefer to unwind the position and diversify your holdings. Tax loss harvesting or tactically trimming may be a better route to explore. Or, both approaches may work.
Again, you have choices, and that's why we believe having a financial professional in your corner is beneficial.

Like what you're reading?
Join the thousands of readers getting stories like this delivered straight to their inbox every Thursday — for free. Give it a spin, enter your email to sign up.
Footnotes
*All information presented herein is for informational purposes only and should not be deemed as investment advice or a recommendation to purchase or sell any specific security. The securities identified and described in this article do not necessarily represent the securities purchased or sold for our portfolios. You should not assume that an investment in these securities was or will be profitable, and there is no assurance, as of the date of this presentation, that the securities have been or will be in any model portfolio. All information expressed in this article is subject to change without notice. There is no representation or guarantee that any opinion, estimate or projection will be realized. The information is believed to be reliable at the time of publication of this article in May 2023; however no representation or warranty is made concerning its accuracy. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. All investments involve risk and may lose money (including principal).
1Jstor.com, Oct 1997
Related Articles

3 Ways to Lower Income Tax in Retirement
Even if you’re not working in retirement, you probably generate income and pay tax on it. How, you...

What Every Retiree Should Know About Taxes
Tax planning doesn’t end with retirement. In fact, tax planning can be equally, if not more...

How Much Risk Can or Should You Take With Your Investments?
Has the recent pullback in the market found you wondering if your risk level is set correctly for...
.jpg)